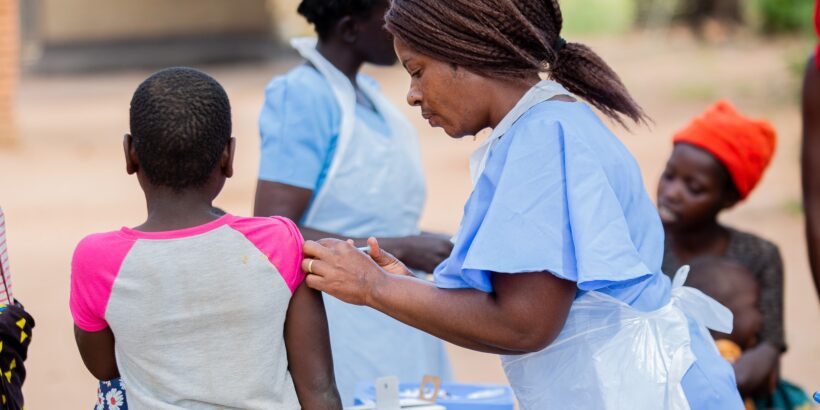
Malawi’s integrated typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV) introduction campaign in May 2023 was the culmination of years of national leadership on typhoid surveillance and vaccine research, followed by a series of challenges turned into opportunities.
Long before the world turned upside down during the COVID-19 pandemic, policymakers and partners in Malawi reviewed typhoid burden data, discussed previous typhoid outbreaks, and considered the increasing risk of typhoid due to drug resistant strains and intensifying climate change catastrophes. The forward-thinking paid off: plans for the TCV campaign, approved by Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, began in earnest as polio and measles gained ground against immunization programs beset by COVID-related interruptions.
This presented an opportunity – not only to meet children with the new TCV, but to stem the growing tide of outbreaks and reach children with routine antigens and interventions that were missed during the pandemic: in this case, measles-rubella (MR), bivalent oral polio vaccine (bOPV), and Vitamin A supplementation.
At the end of the campaign, more than 7 million Malawian children had been reached with TCV. Now, nearly one year later and with TCV available (alongside MR and bOPV) in routine immunization, we’ve reflected on critical components for policymakers to consider before implementing an integrated campaign:
- Aligned political will of national stakeholders and partners for immunization, including new introductions, to set the tone for campaign planning early on
- Consistent and reliable multilateral and national partner support to provide coordination, consistency, and critical stop-gap support to national governments
- Sufficient capacity of the local financial unit to swiftly meet the complex financial demands of multiple partners working across antigens
- Early, proactive, ongoing communication and community social mobilization to explain the interventions and rationale behind integration, reassure safety, and dispel rumors and misinformation
- Campaign staff with ample resources and willingness to accommodate the demands of delivering simultaneous interventions
- Streamlined data collection tools, such as a single tally sheets, to ease the burden of campaign staff
TCV introduction – or any new vaccine introduction – is an opportunity to offer additional antigens that may have been previously missed. An integrated campaign capitalizes on much of the partnering and planning that goes into every campaign. However, there are many factors to be considered to ensure integration is a worthwhile and successful undertaking.
As more policymakers consider strategies for efficient new vaccine introduction, the experience from Malawi provides foundational information on the factors for a successful integrated campaign. Read more reflections here.
Cover Photo: A health surveillance assistant administers a vaccine in rural Lilongwe. Credit: TyVAC/Madalitso Mvula.